The Imperative for Integrated Battery Design in EVs
Electric vehicle (EV) batteries have come a long way. From bulky, standalone modules to sleek, highly integrated packs, the evolution of battery design is pivotal for better performance and efficiency. Early EV batteries used simple modular assemblies, which limited energy density and added unnecessary weight. Today, integrated battery systems combine cells and modules into compact, cohesive packs that maximize energy storage while reducing size and complexity.
Why does integration matter? It means improved energy density, better thermal management, and simplified manufacturing — all essential for longer driving ranges and safer EVs. Higher integration also drives down costs, helping EVs become more affordable and accessible.
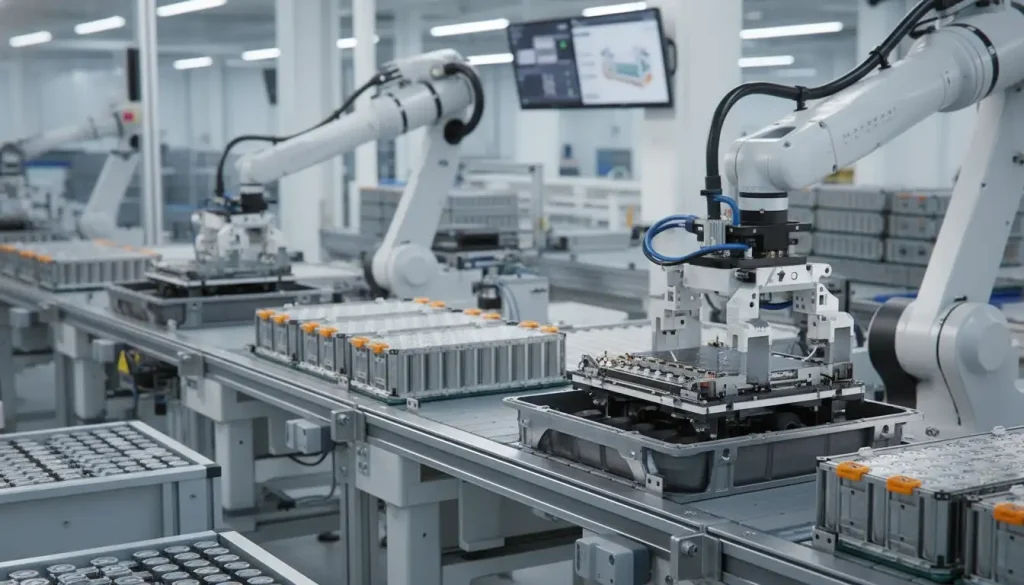
LEAPENERGY is at the forefront of this shift. With a deep understanding of both modular design and pack-level integration, they lead the transition from traditional cell-to-module (CTM) layouts to advanced cell-to-pack (CTP) architectures. This move streamlines the battery system, boosting efficiency and performance without compromising reliability.
In short, integrated battery design isn’t just a trend—it’s critical for the future of electric vehicles. And LEAPENERGY’s innovative approach is helping reshape how we think about EV battery packs, making high-performance, cost-effective electric driving a reality today.
Understanding Battery Module Fundamentals
At the heart of EV battery systems lie the battery modules. These modules are made up of several individual cells grouped together, forming the building blocks before moving to pack integration. Traditionally, battery modules use the Cell-to-Module (CTM) architecture, where cells are organized inside a protective casing with supporting wiring and cooling elements.
Core Components in Battery Modules
- Cells: The core energy units—typically lithium-ion—arranged in series and parallel for the needed voltage and capacity.
- Module Housing: A sturdy case that protects cells from physical damage and helps with thermal management.
- Interconnects and Busbars: Electrical pathways connecting cells within the module to maintain efficient power flow.
- Thermal Management Systems: Cooling plates or channels that keep temperatures stable to maximize performance and longevity.
- Battery Management System (BMS): Sensors and control electronics monitoring cell health, temperature, and charge levels.
Traditional CTM Architecture
In the CTM setup, individual cells are assembled into modules that can be tested and replaced as one unit. This approach simplifies manufacturing and serviceability but adds some extra weight and volume due to protective casings and interconnections between modules.
Design Best Practices
- Modularity: Designing modules for easy assembly and disassembly helps with maintenance and upgrades.
- Thermal Efficiency: Incorporating effective cooling solutions within the module avoids hotspots and extends battery life.
- Mechanical Stability: Robust housing and vibration resistance ensure durability, especially in rough driving conditions.
- Standardized Interfaces: Using common electrical and mechanical connections speeds up manufacturing and repairs.
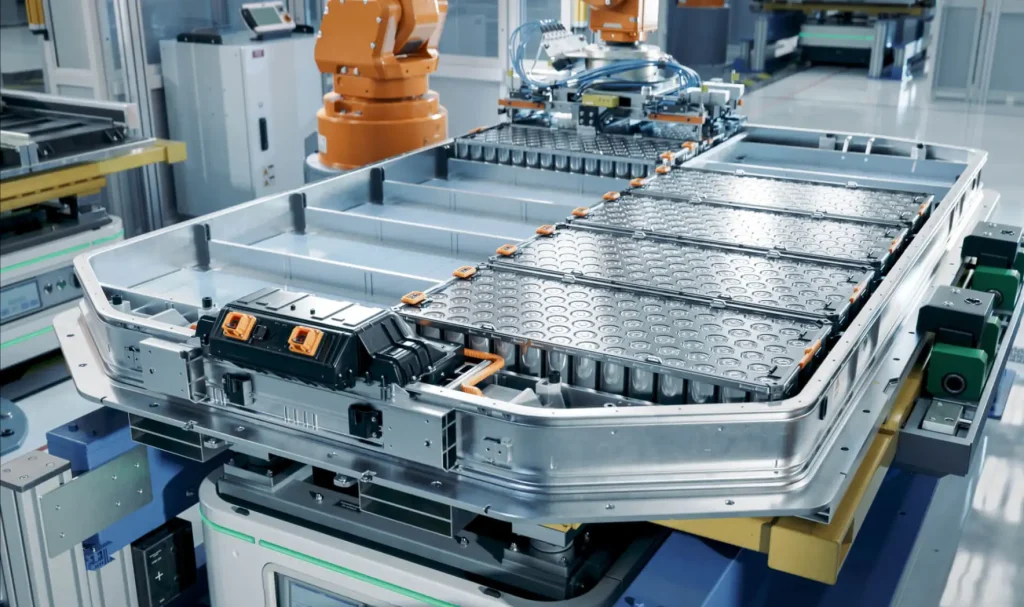
Modular Case Study: LEAPENERGY’s Approach
LEAPENERGY has been refining battery modules by balancing strong protection with minimal added weight. Their modular designs highlight ease of assembly with optimized thermal pathways, allowing US automakers to streamline production while meeting local safety standards. By focusing on these fundamentals, LEAPENERGY prepares the modules not just for standalone use but as key parts in moving toward full pack integration.
Understanding these basics of battery module design sets the stage for exploring how modern EV systems are shifting from modules to bigger, more integrated packs without losing reliability or safety.
The Shift to Pack-Level Integration
As EV battery tech evolves, we’re seeing a major shift from traditional cell-to-module (CTM) setups to more integrated architectures like cell-to-pack (CTP) and cell-to-chassis (CTC). Each approach impacts how batteries are built, how space is used, and ultimately how much power and range your EV can deliver.
- CTM (Cell-to-Module): Cells are first grouped into modules, then modules form the pack. This is the classic design—easy to service but adds weight and size because of extra components.
- CTP (Cell-to-Pack): Cells skip the module stage and connect directly into the pack. This trims weight and improves energy density, making packs smaller and more efficient.
- CTC (Cell-to-Chassis): Cells are integrated directly into the vehicle chassis, cutting down extra packaging parts and maximizing space even further.
The main driver behind moving to pack-level integration is efficiency. More integration means lighter packs, better thermal management, and overall improved performance—all critical for EVs in the U.S. market, where range and reliability are top priorities.
Of course, switching to CTP or CTC brings challenges such as thermal control, safety protocol updates, and more complex pack designs. That’s where LEAPENERGY steps in with our hybrid CTP technology—a smart middle ground combining modular serviceability with the high density and efficiency of pack-level integration. This approach keeps manufacturing flexible while delivering the lightweight, high-power packs that American drivers want.
Advanced Technologies Driving Integration
When it comes to boosting integration in EV battery packs, advanced tech is the game-changer. At LEAPENERGY, we focus heavily on cell-to-pack (CTP) cell fixation methods that improve pack stability and reduce weight. Unlike traditional designs that rely on modules, CTP lets cells fit directly into the pack structure, trimming excess materials and improving energy density.
Here’s what’s shaping the future:
Cell Fixation Innovations: New adhesives, welding techniques, and mechanical clamps secure cells better while allowing efficient heat dissipation. This means safer, more reliable packs that handle stress without extra bulk.
Emerging Trends in CTC and CTB: Cell-to-case (CTC) and cell-to-board (CTB) architectures are gaining traction. These methods integrate cells even deeper into the battery’s physical structure, cutting down on wiring and connectors. It streamlines assembly and improves thermal management.
Modular Hybrid Solutions: Hybrid designs combine the best of modular and direct integration approaches. LEAPENERGY has developed proprietary systems that maintain serviceability while maximizing pack density. This balance helps meet U.S. market demands for both performance and ease of maintenance.
LEAPENERGY’s proprietary technologies also include precision manufacturing processes and smart interconnect designs that enhance both pack durability and electrical performance. By pushing these boundaries, we’re helping shape the future of highly integrated, efficient EV battery packs tailored for American drivers.
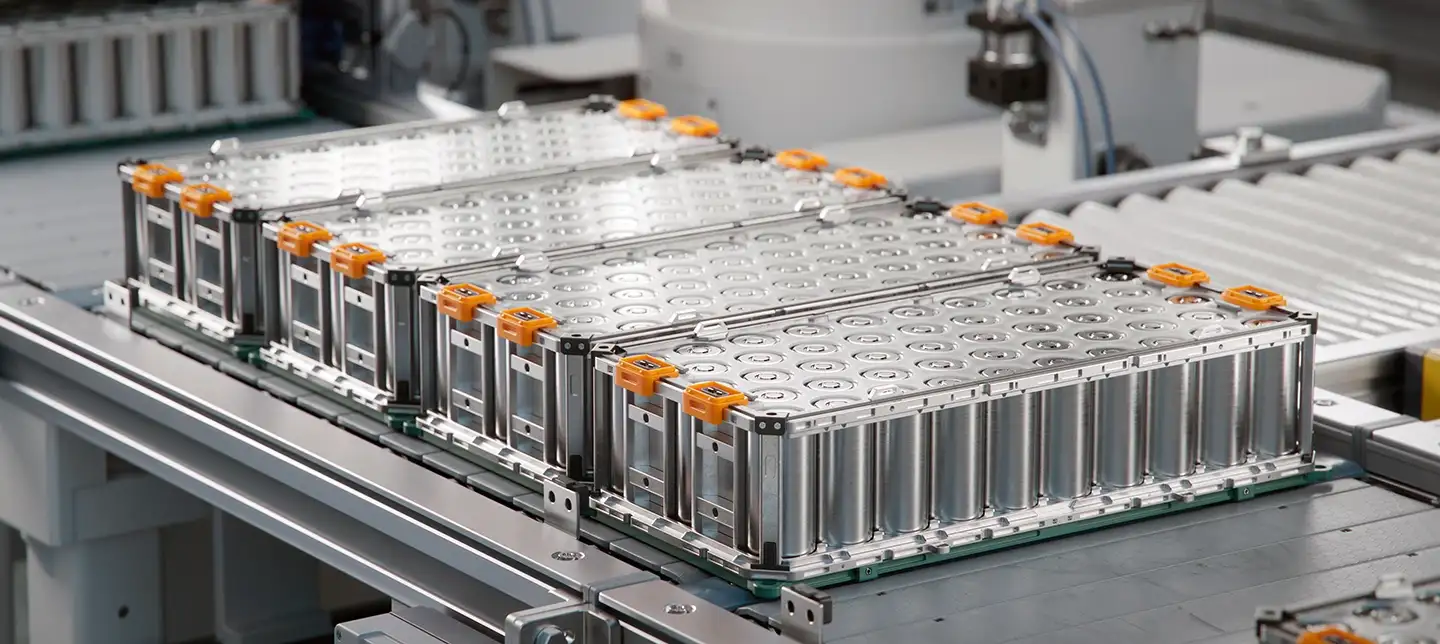

Optimization Techniques for Density, Efficiency, and Performance
When designing EV battery packs, boosting energy density is a top priority. Higher density means longer range and less weight—key for U.S. drivers looking to maximize their electric vehicle’s potential. We achieve this by refining cell arrangement and minimizing empty space through smart EV packaging layouts and advanced modular battery assembly processes.
Efficiency also ties closely to manufacturing workflows. Streamlined production methods reduce costs without sacrificing quality. Lean assembly lines and automation make it easier to build consistent, reliable battery packs at scale. This approach supports better battery pack manufacturing efficiency, helping manufacturers meet growing demand.
Under the hood, performance tuning involves balancing power output, thermal management, and electrical design. Using real-world testing and simulation, we set quantitative benchmarks that measure voltage stability, heat dissipation, and cycle life. These data-driven insights guide improvements that make the battery pack safer, longer lasting, and more responsive on the road.
Key optimization tactics include:
- Tight cell-to-pack assembly reducing unnecessary materials
- Advanced thermal management to maintain optimal operating temps
- Electrical layout refinement for lower resistance and faster charging
- Standardized manufacturing steps to improve yield and reduce defects
By focusing on these areas, we deliver EV battery packs that offer the density, efficiency, and performance U.S. drivers demand — all while keeping production scalable and cost-effective.
Safety and Serviceability in Integrated Battery Systems
Safety is a top priority when designing highly integrated EV battery packs. With the increased energy density and tighter packaging of cell-to-pack (CTP) systems, managing thermal runaway risks becomes essential. LEAPENERGY tackles this using advanced AI-driven battery management systems (BMS) that monitor temperature and voltage in real time, quickly detecting any irregularities before they escalate.
On the service side, LEAPENERGY focuses on modular designs that make battery packs easier to inspect, repair, and replace without dismantling the entire system. This approach not only reduces downtime but also meets strict U.S. regulatory standards for battery safety and serviceability. Features like accessible EV safety venting systems and standardized high-voltage interconnects ensure both user safety and compliance with federal guidelines.