Understanding Automotive-Grade Requirements
Designing automotive-grade battery packs demands meeting tougher criteria than consumer-grade batteries. Unlike consumer batteries, automotive batteries face harsher environments, longer lifespans, and strict safety rules. Here’s how they differ:
| Feature | Automotive-Grade Battery | Consumer-Grade Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Reliable for 10+ years | Designed for shorter use |
| Safety Standards | Complies with ISO 26262, UN 38.3, IEC 62660, SAE J2464 | Basic certifications |
| Performance | Stable cycle life and power delivery | Focus on initial capacity |
| Environmental Tolerance | Operates in extreme temperatures and vibrations | Limited operating range |
Key Standards and Certifications
- ISO 26262: Functional safety for automotive electronics
- UN 38.3: Transport safety for lithium batteries
- IEC 62660: Performance and safety test methods for EV batteries
- SAE J2464: Battery abuse testing for electric vehicles
Performance Benchmarks
For long-term reliability, automotive battery packs must deliver consistent:
- Cycle Life: Sustaining thousands of charge-discharge cycles with minimal capacity loss
- Energy Density: Offering high storage per weight/volume without compromising safety
- Power Delivery: Providing stable output under varying load and temperature conditions over a decade or more
Meeting these automotive-grade requirements ensures batteries not only perform efficiently but maintain safety and reliability throughout the vehicle’s lifespan. This focus is essential for EV battery pack design aimed at the demanding US market.
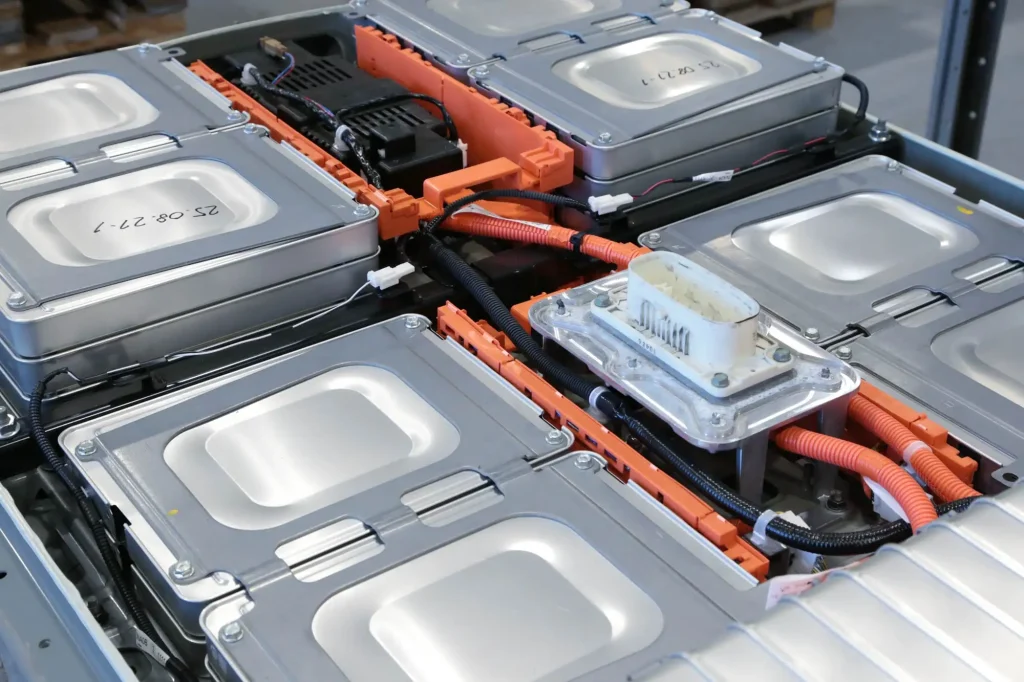

Cell Selection for Maximum Longevity
Choosing the right cells is key to designing an automotive-grade battery pack built for long-term reliability. When comparing chemistries, NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) cells offer high energy density, which means more power and range in a smaller package. However, LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries shine with superior cycle life, thermal stability, and safety, making them a top choice for many EV battery pack manufacturers prioritizing longevity and durability. For a deeper dive into why LFP is often preferred for safety and lifespan, check out our detailed guide on why LFP batteries are best.
In terms of cell formats, cylindrical cells are robust and have proven reliability from decades of use but can be heavier and take up more space. Prismatic cells offer a good balance of packaging efficiency and mechanical strength, often favored in automotive battery packs. Pouch cells provide high energy density and flexibility but require thorough protection against swelling and mechanical stress to maintain reliability over time.
Long-term performance depends on managing capacity fade, internal resistance growth, and calendar aging:
- Capacity fade reduces overall battery range after many charge cycles.
- Internal resistance rise leads to heat generation and decreased efficiency.
- Calendar aging results from chemical and physical changes even when idle over years.
Selecting the right chemistry and cell format while addressing these factors is crucial for crafting EV battery packs that deliver consistent performance over 10+ years. Balancing energy density and longevity is a smart move for buyers looking for reliable, safe, and durable automotive-grade battery packs.
Structural and Mechanical Design Principles
Designing automotive-grade battery packs starts with a strong focus on structural and mechanical integrity. Enclosure materials must be tough enough to handle impacts and meet crashworthiness standards, protecting the cells during collisions. Using lightweight but durable materials like aluminum or reinforced composites helps balance protection with vehicle efficiency.
Vibration is another big challenge. Batteries in electric vehicles face constant mechanical stress on the road, so vibration isolation systems are crucial to prevent damage and capacity loss over time. Many manufacturers adopt modular architectures that allow for easier maintenance and reduce stress by isolating individual modules.
Recent trends in EV battery pack design highlight cell-to-pack (CTP) and cell-to-body (CTB) integration. These methods improve pack rigidity and efficiency by removing some traditional components, reducing weight, and boosting space utilization. CTP and CTB designs help enhance both durability and thermal management by creating a more compact and robust battery system.
For more on the latest advancements in packaging and mechanical design, the detailed insights on modular vs. integrated EV battery pack architectures offer a great overview. Additionally, the module-to-pack integrated EV battery systems page dives deeper into how these integrations improve reliability and performance.
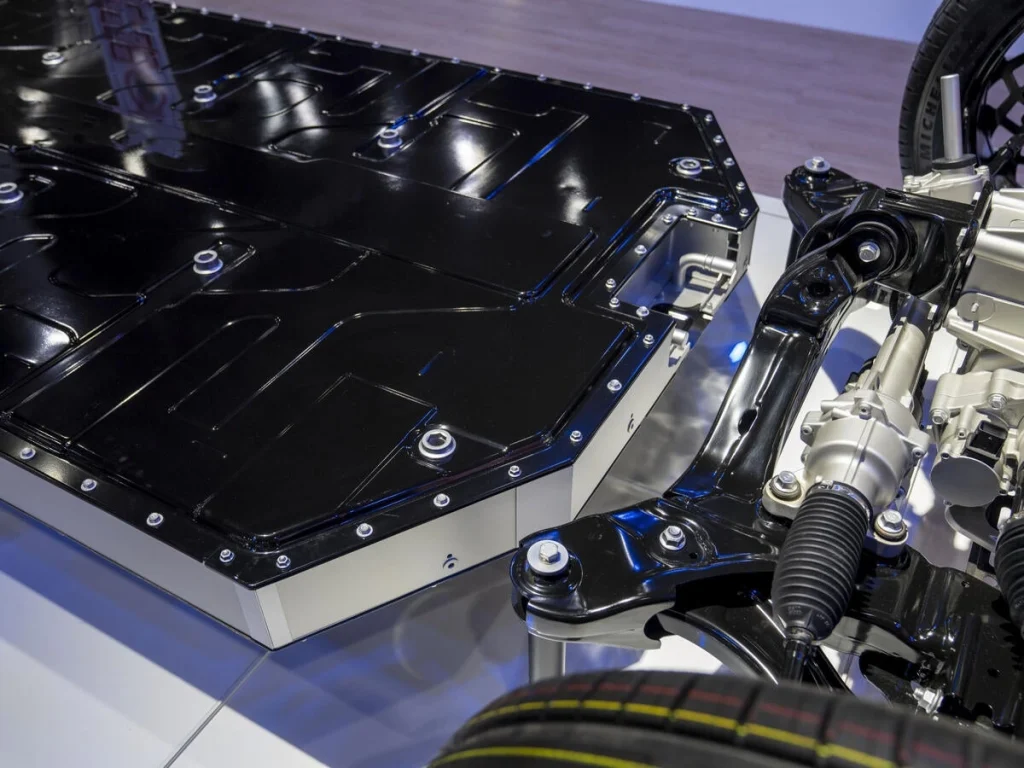

Advanced Thermal Management Systems
Keeping an automotive-grade battery pack at a consistent temperature is crucial for long-term reliability. Uneven heat can cause hotspots, speeding up battery degradation and reducing cycle life. That’s why uniform temperature control isn’t just nice-to-have—it’s essential to maintain performance and safety over the battery’s lifespan.
There are several cooling methods used in EV battery pack design:
- Air cooling: Simple and cost-effective, but less efficient in managing high heat, especially under fast charging or heavy load.
- Liquid cooling: Superior for heat dissipation, widely used in automotive-grade batteries to maintain optimal cell temperatures during extreme conditions.
- Phase-change materials (PCM): These absorb and release heat as they change states, providing passive thermal regulation and adding an extra layer of protection from temperature spikes.
Designing thermal management systems also means planning for extreme climates—whether it’s the freezing cold winters of the Midwest or the scorching heat of Arizona. Fast charging ramps up heat generation, so cooling systems must handle rapid temperature rises without compromising battery health.
For a detailed comparison on modern cooling techniques used in EV battery packs, exploring innovative options like liquid, air, and hybrid systems, check out this resource on liquid, air vs hybrid cooling for EV battery.
Effective thermal management directly impacts the battery’s longevity, safety, and overall cost-effectiveness, making it one of the top priorities in automotive battery pack design.
Battery Management System (BMS) Integration
A reliable Battery Management System (BMS) is at the heart of every automotive-grade battery pack design. Its core functions include constantly monitoring the state-of-charge (SOC) and state-of-health (SOH) of each cell to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The BMS also performs cell balancing to prevent uneven degradation and fault detection to catch issues early before they escalate.
To boost long-term reliability, modern BMS features predictive diagnostics that anticipate potential failures, helping avoid costly downtime. Overcharge and over-discharge protections are essential safeguards that prevent damaging the battery, especially under harsh driving conditions or fast charging.
Integration with vehicle communication networks like the CAN bus ensures seamless data exchange between the battery pack and the car’s control systems. This connectivity is vital for maintaining safety, managing energy flow, and maximizing overall battery pack cycle life. For a deeper dive into how these systems fit into broader EV battery pack designs, consider reviewing our detailed EV battery pack guide.
In sum, a well-integrated BMS not only protects the battery but also enhances its durability and functional reliability throughout the demanding life of an automotive battery pack.
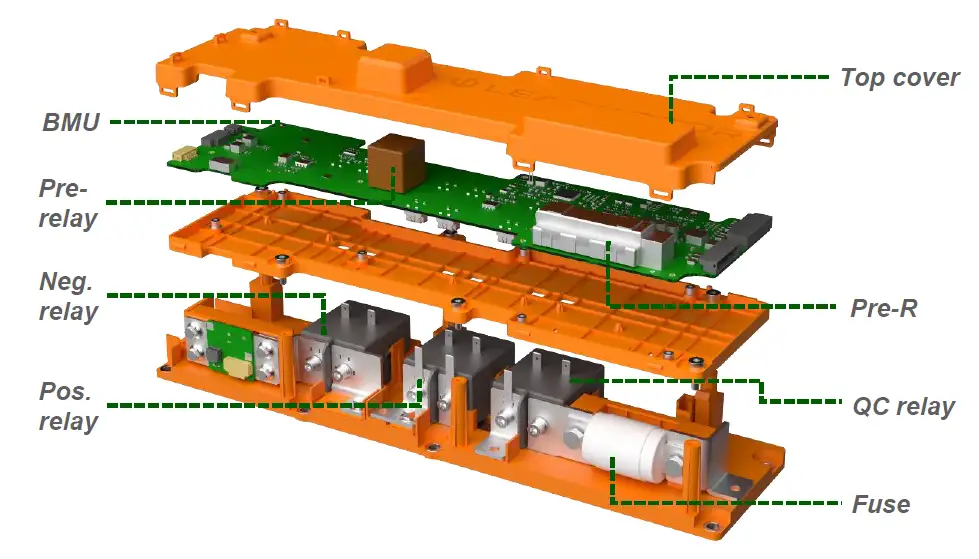
Electrical Architecture and Safety Features
Designing a reliable automotive-grade battery pack starts with a robust electrical architecture focused on safety and performance. Here’s what matters most:
Key Components
- High-voltage interconnects: Must handle heavy current loads securely without overheating or failure.
- Fusing & contactors: Provide reliable circuit protection and quick disconnection during faults or emergencies.
Preventing Thermal Runaway
Thermal runaway is a top safety risk in EV battery packs. Effective prevention includes:
- Venting: Allows hot gases to escape safely, reducing pressure buildup inside the pack.
- Isolation: Separates cells and modules to stop heat spread when one cell fails.
- Fire suppression: Integrated materials or systems that can extinguish or slow down fires quickly.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) & Leakage Protection
- EMC design ensures the battery pack doesn’t interfere with vehicle electronics or external devices.
- Leakage protection prevents current leakage that could cause shorts or shocks, enhancing overall safety.
| Safety Feature | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High-voltage interconnects | Secure current flow | Reliable power delivery |
| Fusing & contactors | Fault protection | Prevents damage or hazards |
| Venting | Pressure & heat relief | Limits thermal runaway spread |
| Isolation | Cell/module separation | Stops chain reactions |
| Fire suppression | Rapid fire control | Protects vehicle and passengers |
| EMC & Leakage protection | Interference and shock prevention | Maintains electronic integrity |
Automotive battery packs built with these electrical and safety standards deliver higher reliability and peace of mind for U.S. drivers. For innovative examples of advanced EV battery pack designs focused on safety and efficiency, explore the range of products from top-tier EV battery pack OEM partners like those at Leapmotor’s product lineup.
Testing and Validation for Real-World Durability
Ensuring long-term reliability starts with rigorous testing and validation of automotive-grade battery packs. Accelerated life testing simulates years of use in a shorter time, identifying potential issues before they arise in the field. Abuse scenarios like overcharging, puncture, and thermal stress help evaluate how the battery withstands extreme conditions. Environmental simulations test performance under temperature swings, humidity, and vibration, reflecting real-world driving environments across the U.S.
Key metrics include cycle testing to track how many charge-discharge cycles the battery endures without significant capacity loss, thermal runaway propagation tests to confirm safety under failure, and vibration endurance to verify that the battery enclosure protects cells during road stresses. These tests ensure the battery pack meets automotive standards and maintains steady performance long term.
For OEMs and EV manufacturers focusing on dependable battery systems, understanding this testing is crucial. You can find insights into how top automotive battery pack manufacturers approach real-world durability to meet strict quality control and regulatory compliance, helping you evaluate suppliers effectively.
Manufacturing and Scalability Considerations
When designing automotive-grade battery packs for long-term reliability, manufacturing consistency and scalability are critical. Best practices include strict quality control measures at every production step to ensure each EV battery pack meets performance and safety standards. Automated testing and precise assembly help reduce defects and improve reliability across large volumes.
Cost optimization is important, but it shouldn’t come at the expense of durability or safety. Modular EV battery architectures are popular because they lower manufacturing complexity and allow easier repairs or upgrades. This approach balances affordability with the robust construction needed for automotive applications.
Lead times and customization options also play a big role for U.S. automakers sourcing battery packs. Working with proven EV battery pack manufacturers who have reliable supply chains means you get faster delivery without sacrificing quality. For insight into trusted suppliers, exploring a list of top global EV battery pack suppliers can provide valuable direction when selecting a partner.
By focusing on scalable manufacturing, modular design, and dependable sourcing, you ensure your automotive battery packs remain competitive, cost-effective, and capable of delivering the long-term reliability drivers expect.