You’ve nailed down the technical specs—voltage, capacity, chemistry. But what if the biggest threats to your battery system procurement aren’t on the datasheet? Too often, hidden risks lurk beneath the surface, sabotaging ROI and project timelines after contracts are signed. This isn’t just about cells and packs—it’s about integration pitfalls, unexpected lifecycle costs, and unreliable suppliers that slip through cracks in engineering change management or certification processes. If you want to avoid costly surprises and ensure your battery setup thrives long term, you need to look beyond specs. Here’s a clear-eyed take on the five hidden risks that could kill your battery system procurement—and how to spot them before it’s too late.
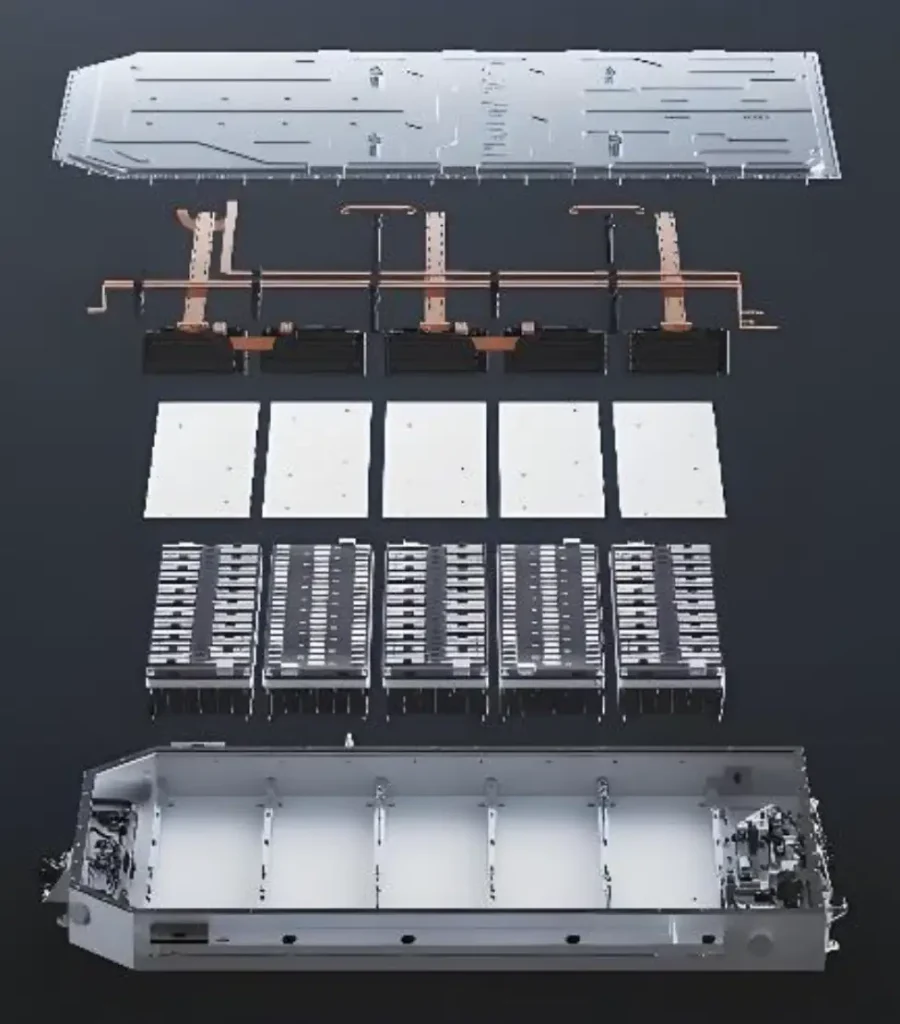
The Procurement Iceberg and Hidden Execution Risks
When sourcing battery systems, it’s tempting to rely heavily on the so-called “golden sample” — that perfect prototype unit which meets every specification on paper. But this leads to a common procurement pitfall: the golden sample illusion. While it represents an ideal, it rarely reflects the reality of full-scale production. The challenges beneath the surface are where hidden execution risks truly lie.
Many procurement professionals focus on technical specifications and overlook critical factors like manufacturing consistency, supplier delivery capability, and quality management system (QMS) audit results. This narrow focus can result in costly surprises during system integration, long-term project lifecycle management, and scalability efforts.
Here’s what you should watch for beyond initial specs:
- Prototype vs. Production Variability: The golden sample might be hand-assembled with extra care, unlike batch production where variability and defects can emerge.
- Supply Chain Stability: Overseas OEM battery system partnerships often carry risks in tier 1 cell sourcing strategy and supply chain resilience that aren’t visible until late stages.
- Cross-functional Coordination: Effective battery system validation process and engineering change management (ECM) require deep collaboration across teams — not evident from a single sample.
- Hidden Costs: Total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis often misses non-recurring engineering (NRE) costs triggered by late-stage design changes or warranty fulfillment challenges.
In short, the procurement iceberg grows larger beyond that single golden sample. Effective sourcing strategies demand a thorough vetting of supplier reliability, manufacturing capacity, and lifecycle cost analysis to mitigate long-term risks. LEAPENERGY’s approach, for example, emphasizes strategic sourcing methodology and lifecycle partnership to address these execution risks early on—making project success far more predictable.
VIEW LEAPENERGY BATTERY PACK TEST PROCUREMENT






Risk #1: The Integration Gap
One of the biggest hidden risks in battery system procurement is the integration gap, especially between the Battery Management System (BMS) and the inverter. Even if each component meets technical specs individually, communication protocol mismatches can derail the whole system. A BMS that doesn’t sync well with the inverter leads to performance drop-offs, safety concerns, and costly delays in validation.
Over-the-air (OTA) software rigidity also adds to this problem. If the software updates aren’t flexible or compatible across devices, it limits your ability to fix bugs or optimize system performance remotely. This can cause long-term headaches for OEM battery system partnerships, where smooth cross-functional engineering coordination is key.
To avoid these pitfalls, pinpoint any communication protocol gaps early, and verify that your supplier supports OTA updates without locking you into rigid software environments. Ensuring alignment reduces execution risks beyond just the specs — a crucial step in the battery system validation process.
For additional insights on integration strategies and cost savings, check out the benefits of battery pack integration that directly impact manufacturing cost and system efficiency.
Risk #2: The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Trap
When procuring battery systems, focusing solely on the upfront price can be a costly mistake. The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) includes more than just the sticker price—it factors in hidden engineering costs, warranty fulfillment, and potential long-term support expenses that easily slip under the radar.
Hidden engineering costs often arise from customizations, integration work, or addressing unforeseen issues during the project lifecycle. For example, Non-Recurring Engineering (NRE) costs linked to design tweaks or compliance adjustments can significantly inflate budgets beyond initial quotes. Additionally, warranty claims might surface not only due to material failures but also from integration mismatches or software bugs—areas where suppliers with weak post-sales technical support infrastructure can cause costly delays.
Ignoring TCO can also obscure challenges tied to lifecycle cost analysis and quality management system (QMS) audits, both critical for ensuring lasting value and minimizing risk. A supplier’s warranty terms combined with their engineering change management (ECM) capability greatly influence how smoothly warranty issues are resolved and how quickly corrective actions roll out.
Before locking in a supplier, dig deeper than the price tag by assessing their ability to manage long-term technical support and cover hidden costs, including those inevitable surprises in compliance or scalability down the line. This approach not only safeguards your project budget but also enhances supply chain resilience and project delivery reliability.
For a comprehensive look at these cost factors in EV battery pack sourcing strategies, check out our detailed EV battery pack guide explained.
Risk #3: Inadequate Engineering Change Management (ECM)
One of the biggest hidden risks in battery system procurement is poor Engineering Change Management (ECM). When suppliers make unnotified swaps—like changing cell suppliers or altering internal components without proper communication—your project faces unexpected setbacks. These undocumented changes often skip vital steps in the battery system validation process, leading to product inconsistencies or failures down the line.
Without a solid ECM process, small tweaks can disrupt cross-functional engineering coordination, resulting in missed design for manufacturability (DFM) opportunities and increased Non-Recurring Engineering (NRE) costs. Over time, these shortcuts inflate your total cost of ownership (TCO) far beyond initial quotes, as warranty claims and reworks pile up.
To avoid these ECM pitfalls, insist on a partner with transparent change notifications and rigorous validation protocols. This keeps your OEM battery system partnership healthy and project lifecycle management on track, especially in complex custom battery pack projects. Ensuring tight ECM helps maintain supplier reliability assessment and preserves the supply chain resilience your U.S.-based operations depend on.
Risk #4: Scalability and Manufacturing Consistency
One of the biggest hidden risks in battery system procurement is the gap between prototype success and mass production realities. A battery pack that works perfectly in small batches or initial samples might hit roadblocks when scaled up. Manufacturing consistency becomes a challenge, especially if your supplier lacks a robust Quality Management System (QMS) or Design for Manufacturability (DFM) processes tailored for volume production.
Capacity constraints can delay your project timeline, forcing compromises or rushed production runs that affect product reliability. This inconsistency often stems from inadequate cross-functional engineering coordination—where prototype designs don’t fully translate into scalable manufacturing setups. Without a clear strategy for scaling production, OEM battery system partnerships can encounter bottlenecks that increase your overall Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
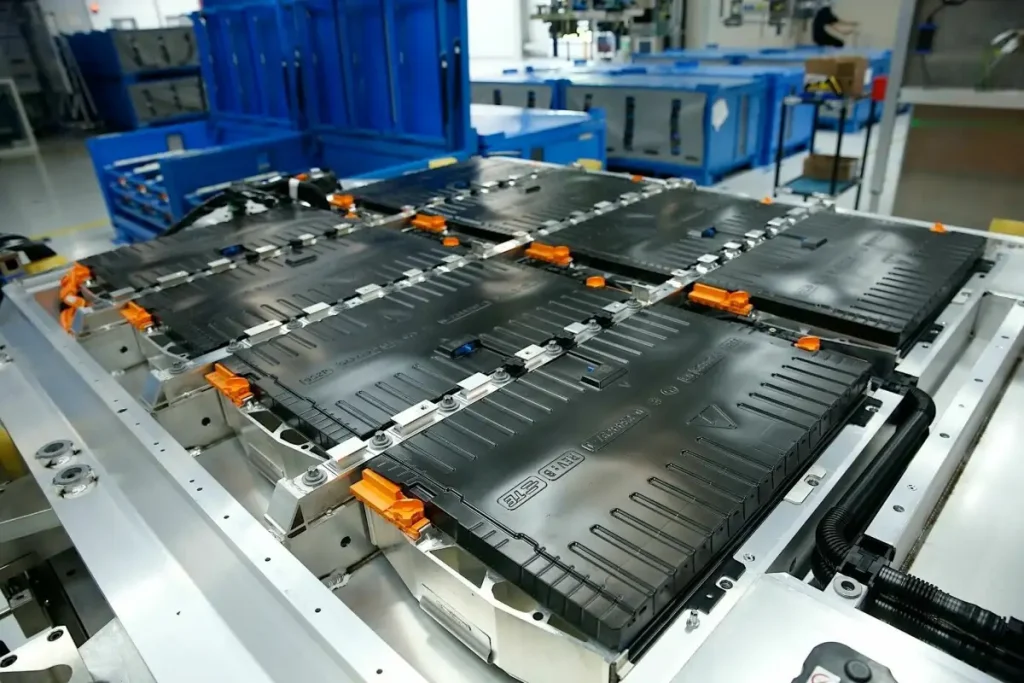

To avoid these pitfalls, focus on suppliers experienced in scaling from prototypes to large-scale production. Check their track record in managing long-term manufacturing capacity and their ability to maintain process consistency across batches. For a deeper dive into how to evaluate this capability, explore insights on scaling EV battery pack manufacturing from prototype to mass production. This kind of due diligence helps ensure supply chain resilience and smooth project lifecycle management without surprises down the road.
Risk #5: Compliance and Certification Readiness vs. Reality
When it comes to battery system procurement, compliance and certification readiness is often where plans hit unexpected snags. A supplier might claim their battery packs are ready for global certifications like UL 2580 or IEC standards, but the reality often includes region-specific hurdles that delay approvals and shipment. These barriers can come from varied local regulations, fluctuating testing requirements, or simply bureaucratic slowdowns in certification bodies.
For U.S.-based companies, this means that even if your battery system supplier boasts global certification readiness, you need to factor in potential delays in obtaining necessary approvals such as UN38.3 transport certification or ISO 26262 safety compliance. These delays can stall your entire project timeline and increase your total cost of ownership (TCO) by adding unexpected compliance costs and time.
To avoid surprises, insist on a battery system supplier with a proven track record in navigating U.S. and international certification landscapes. Regular updates on the certification process and clear visibility into compliance status should be standard during your battery system validation process. Leveraging expert partners familiar with global battery pack standards and regulations will save time and reduce risk. For example, resources like LEAPENERGY’s detailed EV battery pack certification guide offer insights into handling these complex requirements efficiently.
In , understanding that certification readiness on paper rarely matches reality will help you avoid project delays. Build in the extra time and technical support infrastructure necessary to clear these regional certification hurdles smoothly. Working with a supplier who manages compliance rigorously can be a major factor in ensuring your battery system meets all safety, environmental, and shipping standards without last-minute surprises.
VIEW LEAPENERGY BATTERY PACK TEST PROCUREMENT






Mitigation Strategy: How to Vet Your Partner
Navigating the hidden risks in battery system procurement requires a solid vetting strategy for your OEM battery system partnership. Start with a strategic sourcing checklist that covers these critical points:
- Supplier Delivery Capability: Verify stable and scalable manufacturing capacity to avoid surprises affecting project delivery.
- Quality Management System (QMS) Audit: Confirm the supplier’s QMS aligns with industry standards, ensuring consistent product quality.
- Cross-Functional Engineering Coordination: Evaluate how well the supplier manages Engineering Change Management (ECM) and integration between Battery Management System (BMS) and inverters.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis: Look beyond initial pricing to anticipate hidden engineering costs, warranty support, and lifecycle cost analysis.
- Compliance and Certification Readiness: Assess their track record with UL/IEC certifications and readiness for regional regulatory challenges.
- Post-Sales Technical Support: Ensure robust support infrastructure is in place for troubleshooting and long-term partnership success.
LEAPENERGY’s lifecycle partnership approach embodies these best practices, focusing on seamless integration, design for manufacturability, and ongoing validation throughout the project lifecycle. Their commitment to supply chain resilience and battery system validation process makes them a reliable partner for custom battery pack projects.
For a deeper understanding of integration challenges and how strategic sourcing can improve battery system outcomes, explore how the battery unit integrates with the BMS to enhance EV battery safety.
Adopting this comprehensive vetting strategy helps reduce long-term risks and ensures your battery system procurement aligns with American market demands for quality, scalability, and regulatory compliance.