The Environmental Imperative for Sustainable EV Battery Design
Electric vehicles (EVs) are key to reducing our carbon footprint, but their battery packs come with environmental challenges that need urgent attention. EV battery lifecycle impacts—from mining to production, use, and end-of-life—pose significant concerns for sustainability.
Lifecycle Impact Overview
| Stage | Environmental Concerns |
|---|---|
| Mining | Resource scarcity, habitat disruption |
| Production | High emissions, energy-intensive processes |
| Use | Battery degradation, energy consumption |
| End-of-life | Low recycling rates, waste management issues |
Mining lithium, cobalt, and nickel strains natural resources and creates ecological damage. Manufacturing EV battery packs generates substantial greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change. Additionally, current recycling rates remain low, leaving valuable materials underutilized and increasing landfill waste.
Key Challenges
- Resource Scarcity: Lithium, cobalt, and nickel are limited and unevenly distributed worldwide.
- Manufacturing Emissions: Energy-heavy production results in a notable carbon footprint.
- Recycling & Waste: Less than 10% of lithium-ion batteries are currently recycled efficiently.
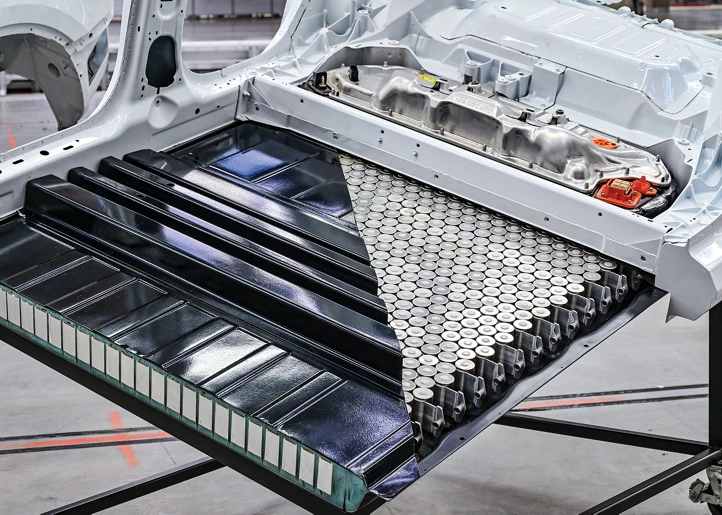

Benefits of Sustainable Battery Design
Sustainable design isn’t just good for the planet—it makes practical sense for the EV industry and consumers alike:
- Lower Carbon Footprint: Better design reduces emissions across the battery lifecycle.
- Reduced Virgin Material Dependence: Using recycled and abundant materials cuts the need for new mining.
- Circular Economy Support: Designing for recycling keeps valuable materials in use longer, creating a closed-loop system.
By focusing on sustainable EV battery design, we can tackle these environmental challenges head-on—making EVs truly green from start to finish.
Core Principles of Design for Recyclability and Sustainability
Designing EV battery packs with recyclability and sustainability in mind starts with building modular and disassemblable pack architectures. This approach allows for easy separation of individual modules and cells, making end-of-life processing smoother and more efficient. By designing packs that can be taken apart without damage, we can significantly boost recycling rates and reduce waste.
Standardization is another key principle. Using standardized components, connections, and battery chemistries simplifies recycling processes by allowing recyclers to handle materials more predictably. This also supports easier maintenance and upgrades, extending battery life and reducing environmental impact.
Choosing eco-friendly adhesives, fasteners, and clear labeling helps speed up disassembly. These materials ensure that batteries can be safely and quickly broken down without releasing harmful substances or requiring complex tools.
Lastly, minimizing hazardous substances and prioritizing recyclable or low-impact materials throughout the pack reduces environmental risks. Selecting materials that are both effective and easier to recover supports a truly sustainable circular economy for EV battery packs.
For a deeper dive into modular and integrated designs that support recyclability, explore LEAPENERGY’s modular vs integrated EV battery pack solutions. These innovations set a strong foundation for sustainable EV battery design and recycling.
Material Selection Strategies for Enhanced Sustainability
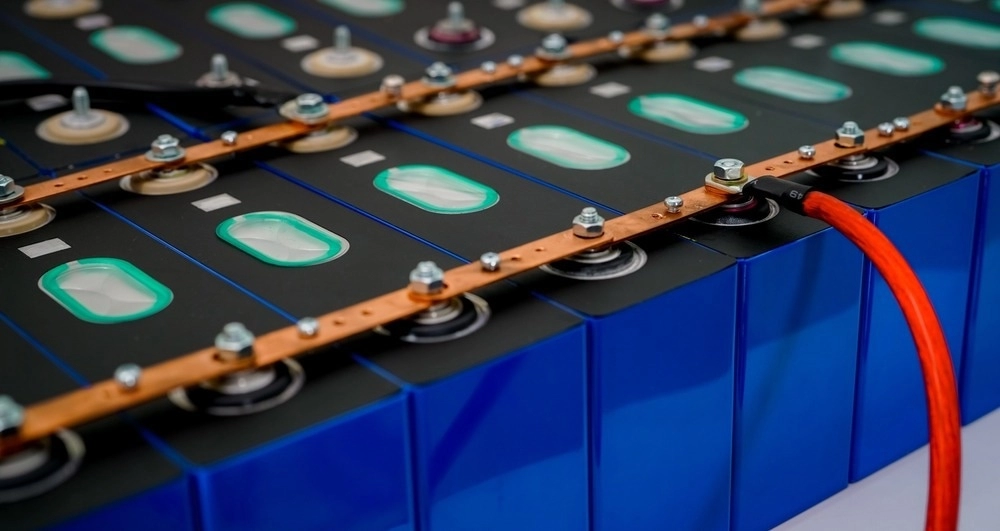

Choosing the right materials is key to designing EV battery packs that are both sustainable and easy to recycle. One major trend is shifting toward low-cobalt or cobalt-free chemistries, like lithium iron phosphate (LFP) instead of nickel manganese cobalt (NMC). LFP batteries reduce reliance on scarce and conflict-prone materials, lowering environmental and social impacts without sacrificing safety or lifespan.
In addition, incorporating recycled content into new battery packs helps close the material loop, reducing demand for virgin mining and cutting overall carbon footprints. Using materials with high recovery potential and low toxicity is crucial to maximize recycling efficiency and protect communities near the supply chain.
At LEAPENERGY, we take a tailored approach by designing custom EV battery packs that balance material efficiency with recyclability. Our packs prioritize components and chemistries optimized for both performance and sustainable end-of-life management. This aligns with today’s push toward circular economy EV batteries, helping U.S. manufacturers meet stricter environmental regulations and consumer expectations.
For a deeper look at design innovations, check out our insights on advanced EV battery pack platforms and technologies.
Enabling Second-Life Applications Through Smart Design
Designing EV battery packs with second-life use in mind is a smart way to boost sustainability and get more value from materials. By creating packs that can be easily remanufactured or repurposed—such as for stationary energy storage or supporting the power grid—manufacturers help extend battery life beyond automotive use.
Key to this approach is incorporating robust diagnostics and state-of-health monitoring systems into the battery pack design. These give clear insights into cell performance and safety, making it easier to evaluate which packs qualify for second-life applications without risking failure.
Several successful second-life projects show clear environmental and economic benefits, like lowering the demand for new battery materials and reducing waste. However, challenges remain, including balancing extended usable life with the need for easy disassembly and recycling when the pack finally reaches end-of-life.
Smart pack designs that plan for these stages ensure we maximize resource efficiency while preparing for effective end-of-life battery management. For more about innovative design strategies in the EV market, check out the insights on EV battery pack design and manufacturing.
Advanced Recycling Considerations in Pack Design
Designing EV battery packs with advanced recycling in mind is essential to boost material recovery and reduce environmental impact. Effective pack designs need to align with recycling methods like pyrometallurgy, hydrometallurgy, and direct recycling to maximize the retrieval of valuable metals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
Key design features to improve recyclability include:
- Easy separation of cells and modules to support automated disassembly
- Clear labeling of materials and components to streamline sorting
- Use of standardized components and connectors compatible with recycling processes
These approaches help push material recovery rates above 95% for critical metals, significantly lowering the demand for virgin materials. Collaborating with recyclers early in the design phase ensures that EV battery packs meet practical recycling needs, enabling more efficient end-of-life processing.
Emerging technologies like automated disassembly lines and improved black mass recovery methods are shaping the future of EV battery pack recycling. Incorporating these innovations during the design stage paves the way for a sustainable circular economy in lithium-ion battery manufacturing.
For more on selecting the right battery packs, check out our guide on top 10 questions to choose EV battery pack.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Drivers
The regulatory environment for EV battery packs is tightening worldwide, with major players like the EU and the U.S. leading the way. The EU Battery Regulation sets strict rules on recyclability targets and requires a minimum percentage of recycled content in new batteries. Meanwhile, U.S. policies offer incentives focused on sustainable battery production and extended producer responsibility (EPR), pushing manufacturers to take accountability for end-of-life battery management.
These regulations aren’t just red tape—they’re driving real change. Battery pack designers and manufacturers need to meet these standards by improving EV battery recyclability and incorporating recycled battery materials right from the design phase. This means focusing on design for recycling principles that simplify end-of-life processing and reduce reliance on virgin resources.
To stay ahead, companies like LEAPENERGY are future-proofing their custom EV battery packs with modular designs and materials that comply with evolving requirements. This approach not only ensures compliance but also supports a true circular economy for EV batteries in the U.S. and abroad. For a closer look at innovative pack designs that meet these standards, check out LEAPENERGY’s latest CTP and CTC technologies.
LEAPENERGY’s Innovations in Sustainable Battery Pack Design
LEAPENERGY stands out in designing EV battery packs that prioritize recyclability and sustainability. Their proprietary approach focuses on modular custom packs that simplify disassembly and enhance material recovery. By building packs with high-recyclability features—such as standardized components and eco-friendly materials—they make every stage of the battery lifecycle more efficient and less wasteful.
In addition to design, LEAPENERGY actively partners with recycling firms and second-life application developers to extend battery value beyond automotive use. These collaborations enable batteries to be repurposed for stationary storage or grid support, further supporting the circular economy. You can see these innovations in action in custom battery packs used in automotive applications that deliver both performance and greener lifecycle metrics.
LEAPENERGY also commits to working closely with OEMs, tailoring sustainable EV battery pack solutions that meet evolving regulatory standards and sustainability goals. This strong partnership approach helps reduce environmental impact while maintaining competitive cost and lead times — essential for the U.S. market’s growing EV demand.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Designing sustainable EV battery packs for recycling faces real hurdles. Cost remains a major barrier—advanced materials and modular designs can increase upfront expenses, making it tough for some manufacturers and consumers. Standardization gaps add complexity too; without uniform component designs and chemistries, recycling processes remain inefficient and costly. Meanwhile, supply chain issues for critical materials like lithium and cobalt create uncertainty in sourcing sustainable raw inputs.

On the bright side, ongoing technological advances offer promising solutions. Improved battery chemistries and innovative pack architectures are driving material efficiency and easier disassembly. Industry collaboration is also gaining momentum, encouraging shared standards and recycling infrastructure investment. Together, these moves will help scale second-life applications and streamline end-of-life management.
Looking ahead, the vision is clear: a fully circular EV battery ecosystem where materials continuously flow from production to reuse and recycling with minimal waste. Achieving this requires overcoming today’s challenges through smart design, cooperation, and regulatory support—paving the way for sustainable, recyclable custom EV battery packs that serve the U.S. market and beyond.